What Is Web 3.0? — A Comprehensive Guide
Jerry Wallis
15 min read

What in the world is Web 3.0? If you’re like most business owners, you might have heard this term tossed around a lot but might not really know what it means. Don’t worry; you’re not alone!
This blog article will give you a detailed introduction to Web 3.0 so you can better understand the hype. Keep reading to learn more about the internet of the future.
Something Exciting Is Happening! 🏃♂️
Imagine a world where . . .
Your digital assistant is always at your service. Suppose you wish to check the availability of groceries in your kitchen. In that case, you can ask your digital assistant to examine the contents of your fridge or pantry by communicating with the interconnected smart devices at your house. Then the device will report back to you with the results. In some cases, it will even order things online on your behalf. Does that sound like something you would embrace or be wary of?
Welcome to the Future of the Internet! 🤖
Coined by John Markoff, a reporter for The New York Times, “Web 3.0” is the third generation of web development and design. It focuses on the user experience and how web applications can be more interactive, intuitive, and engaging. Web 3.0 also emphasises the need for data to be more accessible and open-source to be used anywhere.

In other words, web 3.0 is the latest internet technology that helps machine learning, artificial intelligence, and blockchain achieve real-world human communication by allowing individuals access to their data while compensating for time spent online.
This new generation of web development has already begun to change the way businesses operate. For example, web 3.0 applications are being used to create decentralised marketplaces where buyers and sellers can connect directly without going through an intermediary. This allows for faster transactions, lower fees, and more privacy.
But wait, before we delve deeper into the world of web 3.0, let’s take a quick history lesson.
Before Web 3.0, There Was Web 2.0 🌐
Darcy DiNucci first coined the term “web 2.0” in 1999 in her article “Fragmented Future,” as the term explains the second generation of web development and design (1999-2012).
Web 2.0 refers to web applications that allow users to interact and collaborate with each other online. These applications are typically more user-friendly and intuitive than their predecessors.
Web 2.0 sites are often built around social networking concepts, which allow users to connect and share information. Some famous examples of web 2.0 sites include Facebook, Twitter, and Wikipedia.
Benefits of web 2.0 include enhanced communication and collaboration, more accessible access to information and more democratic participation in the web. Overall, web 2.0 has made the internet a more interactive and user-friendly place, but it is slowly being replaced by web 3.0.
And Before That, Web 1.0 🕰️
Web 1.0 is the first generation of web technology (1989-2005), and it refers to the early days of the internet when web pages were primarily static and text-based.
It all started with Sir Tim Berners-Lee inventing the World Wide Web in 1989 while working at CERN. Soon, with the advent of the internet, many static sites were created whose primary goal was to provide information and nothing more. These days, however, web 1.0 would be considered pretty primitive compared to today’s web standards.
Some of the key characteristics of web 1.0 include:
- Simple, static web pages
- Webmasters created and controlled the content
- Not much user interaction or involvement
- Websites primarily used for information dissemination
These days, web 2.0 and web 3.0 have replaced web 1.0 as the dominant web technology. The higher versions of the web are characterised by more dynamic and interactive web pages and increased user involvement and engagement.
The Basic Components of Web 3.0 📂
Web 3.0 is the third generation of web technology, and it promises to be the most transformative yet. Here’s a look at some of the critical components that will make up this new web:
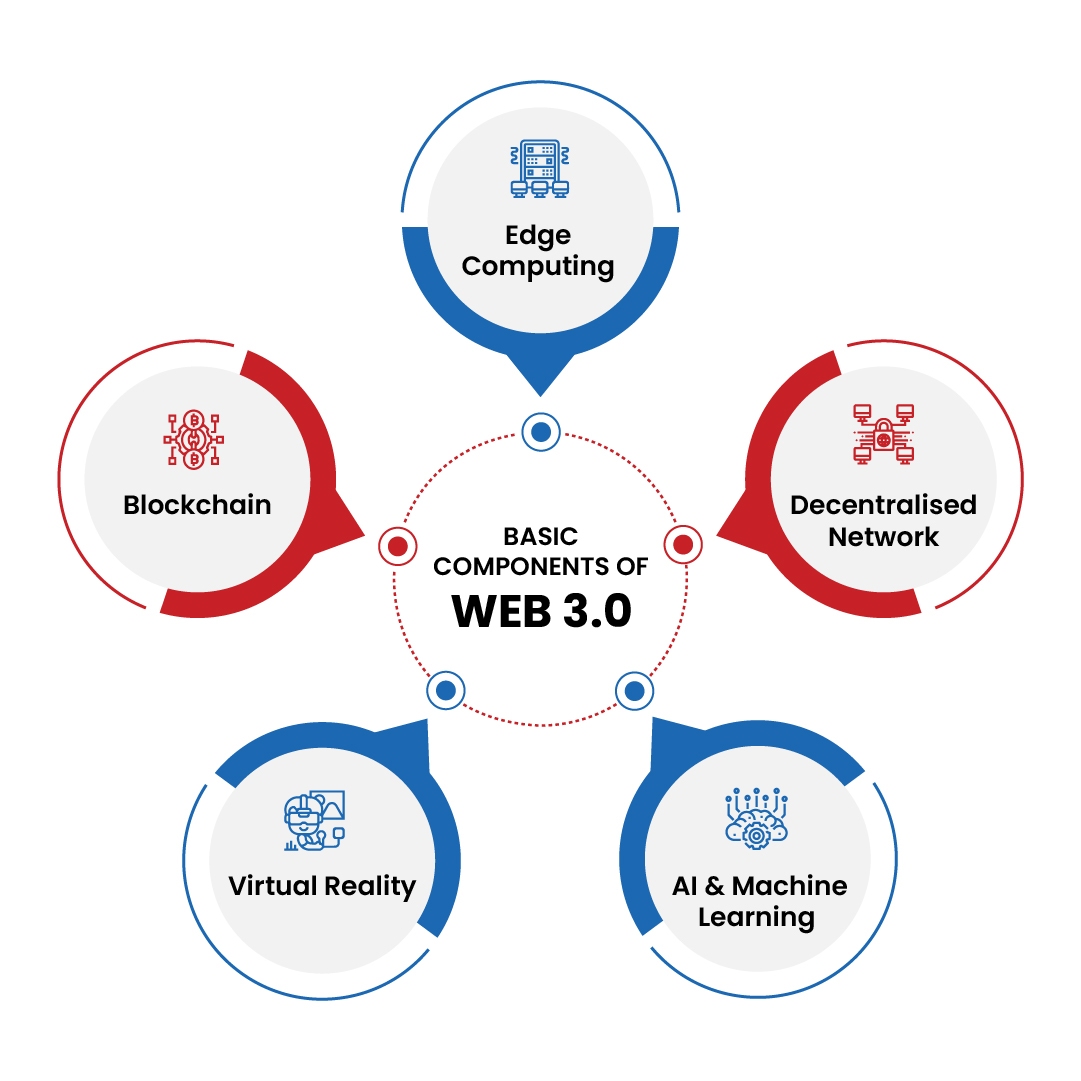
#1 Edge Computing 🖥️
Web 3.0 is the next generation of web technology that promises to revolutionise how we interact with the internet. Edge computing is a new type of computing that allows data and applications to be processed closer to where they are needed instead of in a central location.
The two technologies are often spoken about discussing each other because they share some similarities. Web 3.0 and edge computing aim to make data and applications more accessible and easier to use. They also both have the potential to significantly reduce latency or the time it takes for data to travel from one place to another.
There are some essential differences between web 3.0 and edge computing as well. Edge computing focuses on processing data locally, while web 3.0 is more concerned with creating a decentralised internet. Additionally, edge computing is often used to supplement existing web infrastructure, while web 3.0 is designed to replace it.
Edge computing and web 3.0 are essential emerging technologies that could significantly impact how we use the internet. By understanding how they work and how they differ, we can make more informed business decisions in the future.
#2 Decentralised Network 🕸️
Web 3.0 is the next generation of the web, where instead of centrally controlled web platforms, we have a decentralised web. This means that there is no single point of control or failure and that users are in control of their own data.
A decentralised web is powered by a decentralised network, a computer network that is not all controlled by a single entity. Instead, each computer on the network is equal and can communicate with any other computer.
Decentralised networks are often more secure than centralised ones because there is no single point of attack or failure. They are also more resilient because if one computer on the network goes down, the others can still communicate with each other.
Web 3.0 is the next generation of the web because it enables a new level of interaction between users and web applications. Instead of web applications being controlled by a centralised authority, they are powered by a decentralised network. This means that users control their own data and that a single entity can not shut down web applications.
#3 Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning 🎰
Web 3.0 is the next generation of the web, where the focus is on data and how it can be used to improve our lives. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are two technologies that will play a significant role in web 3.0.
AI is all about making computers more intelligent to do things that humans currently do better. Machine learning is a subset of AI that deals with teaching computers to learn from data. Together, these technologies will help make web 3.0 a reality.
Many examples of AI and machine learning are already being used on the web today. Google uses AI to power its search engine and show users relevant ads. Facebook uses machine learning to suggest friends and groups to users. And Amazon uses both AI and machine learning to recommend products to users.
These are just a few examples of how AI and machine learning will power web 3.0. With the help of these technologies, web 3.0 will be able to do previously impossible things. For more information, check out our detailed article on artificial intelligence and machine learning.
#4 Virtual Reality 😱
The relationship between web 3.0 and virtual reality is still being explored and understood. However, there are many ways in which the two can be used together to create unique and immersive experiences.
Web 3.0 is all about creating a more interactive and personalised web experience. It includes using data to customise the content, using artificial intelligence to provide recommendations, and allowing users to interact with each other directly. Virtual reality, on the other hand, is all about creating an immersive experience that feels real. By combining web 3.0 and virtual reality, we can create experiences that are much more personal and engaging than what is possible with either one alone.
One example of how web 3.0 and virtual reality can be used together is in the creation of virtual worlds. Using web 3.0 technologies to create personalised content and experiences, we can make these virtual worlds feel much more accurate and alive. Another example is in the area of education. By combining web 3.0 technologies with virtual reality, we can create educational experiences that are more immersive and engaging than anything that is currently possible.
The possibilities are endless for combining web 3.0 and virtual reality. As we continue exploring these two technologies’ potential, we will undoubtedly find more ways to use them together to create unique experiences in the days to come.
#5 Blockchain 💸
Web 3.0 is the next generation of the web, where data is more interconnected, and people have more control over their online identities. Blockchain technology is one of the critical components that will power this new web.
Blockchain provides a secure way to store data and transactions. It acts as a shared, immutable ledger for all online transactions and assets. Both tangible and intangible assets, from houses to cars to copyrights to branding, can be tracked and traded on a blockchain network.
In addition, blockchain allows for a decentralised web, where any central authority does not control data. This means that users can have more control over their data and privacy. Web 3.0 will lead to a more open, equitable, and accessible internet for everyone. Blockchain is an essential part of making this happen.
These are just some key components that will make up web 3.0. The web will become more intelligent, personal, and immersive with these new technologies.
How Will Web 3.0 Affect The Way We Do Business? 📋
Web 3.0 is the next stage in the evolution of the internet, and it promises to bring some significant changes to the way businesses operate. Here are a few ways that web 3.0 could affect the way we do business:
- More personalisation: Web 3.0 will make it easier for businesses to personalise their products and services for individual users. This could lead to a more customised and enjoyable experience for customers.
- Greater data security: With web 3.0, businesses can better protect their data from cyber-attacks. This could help to keep customer information safe and secure.
- Improved customer service: Web 3.0 could help businesses provide better customer service by making tracking customer interactions and preferences easier. This could lead to more satisfied customers.
- Increased efficiency: Web 3.0 will allow businesses to automate more processes and tasks. This could lead to greater efficiency and productivity within companies.
Web 3.0 is still in its early stages, so it remains to be seen how exactly it will affect the business world. However, it seems clear that web 3.0 will significantly change how we do business. Thus, web 3.0 could very well be a game-changer for companies worldwide.
If you want to stay ahead of the competition, it’s important to understand web 3.0 and how it will change the business landscape in the years to come.
Web 3.0 – Is It A Blessing In Disguise? 🤔
The internet as we know it is evolving. The new web 3.0 promises to be more user-friendly, decentralised, and secure. But is this new web really a blessing, or will it turn out to be a curse?
On the positive side, web 3.0 will make the internet more user-friendly. Decentralised applications (dApps) will allow users to interact with the web without going through a central authority. This means users will have more control over their data and privacy. In addition, dApps are more resistant to censorship than traditional centralised websites.
On the downside, web 3.0 could lead to even more centralisation of power. Because dApps are decentralised, they are often built on the existing centralised infrastructure, such as web 2.0 applications. This means that the companies that control this centralised infrastructure can still exert much influence over dApps.
In addition, web 3.0 could make it harder for new entrants to compete against established players. Because dApps are often complex and challenging to build, it could be tough for newcomers to get into the market.
So far, web 3.0 is still in its early stages of development. It remains to be seen whether it will truly live up to its promises. However, one thing is for sure: the web is changing, and we must be prepared for what comes next.
Web 3.0 & The Future and Marketing 📈
The future of marketing is bound to be fascinating. With the advent of new technologies, businesses will have to change how they reach and engage their audiences. One significant trend already making waves is the so-called “Internet of Things,” a term used to describe the growing network of physical objects connected to the internet. This trend has implications for marketing.
For one, it will allow businesses to collect a wealth of data about their customers’ habits and preferences. This data can then be used to create highly targeted marketing campaigns that are much more likely to convert leads into sales.
Another implication of the Internet of Things is that marketing campaigns will become increasingly personalised. As more and more devices are connected to the internet, businesses can collect detailed information about individual users. This data can then be used to deliver customised messages that are likely to resonate with each user.
There will also be less focus on keyword optimisation because most of the searches will be voice searches with the help of digital assistants. Marketers will have to optimise their content for specific yet long sentences. Customers will therefore want a hyper-personalised experience.
Customers will no longer read text-based content (such as this one, oops!) but instead want to interact with the content with the help of their favourite digital assistant. They want to “speak with their search engines in their preferred language.” Thus, marketers should spend more time trying to create rich content for the next generation of internet users.
Finally, the rise of the Internet of Things will likely lead to a future in which marketing is more interactive and engaging. For example, businesses may use Augmented Reality (AR) technology to provide their customers with a unique and immersive experience. This could involve overlapping digital content in the real world or providing users with interactive experiences based on their location or preferences.
The future of marketing is undoubtedly an exciting one! With the right strategy, businesses can use new technologies to reach and engage their audiences in previously impossible ways.
Web 3.0 & Blockchain 💰
Web 3.0 is the next generation of the internet, and it’s all thanks to blockchain!
Blockchain provides an open system that allows users to access data differently through artificial intelligence (AI). Blockchain was first created as bitcoin back when crypto wasn’t too popular, but since then has evolved into so much more than just currencies; people now use its technology everywhere, from tracking stocks to trading patent rights.
With web 3.0, we are shifting from the traditional web to a more decentralised web. This is where blockchain comes in. Blockchain provides a way to decentralise web 3.0 applications and data. Essentially, web 3.0 is the next evolution of the internet, and blockchain is the technology that powers it. By using blockchain, web 3.0 can be more secure, efficient, and transparent.
So what does this mean for businesses? Well, if you’re looking to stay ahead of the curve, it’s essential to understand how web 3.0 and blockchain can work together. By understanding this relationship, you’ll be better equipped to take advantage of the opportunities that web 3.0 presents. So let’s understand how web 3.0 and blockchain work together to power the next generation of the internet.
Web 3.0 is all about decentralisation. That means shifting away from centrally-controlled platforms like Facebook and Google and towards decentralised applications (dApps) powered by blockchain. With web 3.0, there is no single point of failure and data is distributed across a network of computers rather than being stored on a central server. This makes web 3.0 much more resilient to attacks and ensures that information is always available when you need it.
Blockchain works by creating a shared ledger of transactions that are stored across a network of computers. This ledger is secured by cryptography, which makes it tamper-proof. Because blockchain is decentralised, it doesn’t rely on any single entity to function. This makes it incredibly secure and resilient to attacks.
So Where Are We Headed? 🚶♀️
The future of the web is here, and it’s a beautiful thing!
People will soon be able to enjoy personalised search results without feeling like their private information has been exposed. Companies can then develop cross-platform technologies that consider customers’ preferences while giving them access to high-quality and hyper-personalised content. This also means better customer service because customers won’t be left out in the cold anymore. Besides, who wouldn’t want more immersive browsing?
The new internet will be here soon, and it’s time to accept and adopt it. If you want to learn more about all the cool stuff, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, blockchain, big data, etc., feel free to write to us for a friendly conversation. We’ll be happy to answer any questions you may have and provide you with more information.
Topics
Published On
July 07, 2022

